What is CMM Machine? Diagram, Principle, Types, and Uses
In modern manufacturing and quality control, ensuring precision in measurements is crucial. Traditional measurement techniques often fail to provide accurate, repeatable, and automated measurement processes. Hence, it results in inaccuracies and possible flaws in the end product. These inaccuracies lead to high production costs, material wastage, and reduced quality standards.
Coordinate Measuring Machines or CMM machines offer an advanced solution. These machines provide accurate size evaluation through a sensing probe to map the exact geometric coordinates of a component. In this article, we will explore the working principle of Coordinate Machines, their applications, different types, and key features.
What is CMM Machine (Coordinate Measuring Machine)?
A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a precision instrument to accurately measures the physical dimensions and geometric characteristics of an object. It operates by detecting discrete points on the surface of a part using a probe and then recording their exact positions in a three-dimensional coordinate system.

These machines are primarily utilized to evaluate a part or structure to verify whether it meets the intended design requirements. Coordinate measuring machines play a vital role in quality inspection and verification to evaluate the accuracy of manufactured parts and maintain quality standards.
Coordinate Measuring Machine Diagram
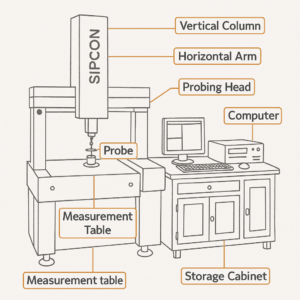
A CMM machine (Coordinate Measuring Machine) comprises various components such as a probe, granite base, bridge structure, and measurement axes (X, Y, Z) for precision results in multidimensional measurement. Here are the components of the Coordinate Measuring Machine Diagram:
Probe Tip/ Stylus
In a Coordinate Measuring Diagram, the probe tip is the sensing element at the end of the probe that communicates with the workpiece surface straightly to collect the data that has been measured.
Granite Table
A granite table provides a stable, vibration-resistant surface for precise measurements. Its thermal stability and rigidity ensure accuracy by reducing deformation and environmental influences during auditing.
Fixtures
A fixture is a holding device that positions and stabilizes the workpiece safely during measurement. It guarantees accuracy and consistency by preventing movement during inspections.
Air Compressors & Dryers
Air Compressors and Dryers are used to supply clean, dry, and pressurized air for CMM operations. They avoid moisture buildup, ensuring stable air-powered regulation, precise measurements, and extended equipment durability.
Software Interface
The software interface is a crucial component that processes measured data and provides a user-friendly platform for analysis. It allows operators to visualize measurements and compare them against design tolerances.
Coordinate Measuring Machine Working principle
A CMM machine (Coordinate Measuring Machine) works based on the three-dimensional coordinate system to accurately measure the physical and geometric characteristics of an object. It utilizes a probing system to inspect and record specific points on the outer layer of components. It helps in maintaining an accurate dimensional assessment.
CMM machines operate based on two fundamental principles. The first relies on a mechanical probe that physically contacts the object to capture measurements. The second utilizes non-contact probes, such as lasers or cameras, to detect and map the workpiece’s point cloud.
How does the CMM Machine work?
A Coordinate Measuring Machine operates by utilizing a probe to capture precise points on an object’s surface. These measurements are then processed by a computer, which calculates and records the object’s dimensions within a 3D Cartesian Coordinate System (Z, Y, and Z axes). Here are the steps to explanation of working of CMM Machine:
Step 1: Positioning the component
- The part that has to be measured is properly placed on the Coordinate machine’s granite base or fixture to guarantee stability.
- The machine introduces a reference coordinate system depending upon the part’s alignment.
Step 2: Probing the Surface
- With the X, Y, and Z axes, the probe moves accordingly with these axes.
- A mechanical touch probe touches the object physically at discrete points.
- Laser or optical sensors capture surface data without contacting directly, generating a point cloud.
Step 3: Capturing coordinate data
- Whenever the probe comes in contact with the components, the Coordinate measuring machine records its accurate position within the 3D coordinate system.
- The machine gathers multiple data points to verify the object’s dimensions and geometry.
Step 4: Processing and Analyzing Data
The gathered measurements are evaluated using CMM software to determine:
- Length, Width, and Height
- Geometric Features (angles, curves)
- Tolerance compliance based on different CAD designs and specifications
Step 5: Making reports and verifying results
- The software produces inspection reports and evaluates measured dimensions against design specifications.
- Makers utilize this data to evaluate quality, identify defects, and enhance production processes.
Features of Coordinate Measuring Machines
A coordinate measuring machine (CMM Machine) is developed to offer high-accuracy measurements for quality assurance and verification. Its key features are explained below:
High-precision measurement
- Maintains extreme accuracy for geometric evaluation.
- Ensures reliable measurement of complex geometries with repeatable accuracy.
- Delivers micron-level precision, reducing errors in crucial dimensional inspections.
Three-dimensional coordinate system
- Operates on X, Y, and Z axes to determine accurate cartesian coordinates.
- Offers 3D Measurements for detailed evaluation and analysis.
- Enables accurate 3D positioning, ensuring comprehensive geometric assessment of difficult parts.
Various Probing Systems
- Contact probes: Probes that physically engage with the surface for measurement accuracy.
- Non-contact probes: Optical, laser, or vision-based sensors for high-speed, contact-free scanning.
- Hybrid systems: Some CMMs combine both contact and non-contact probes for improved versatility and accuracy in diverse applications.
Advanced Software Integration
- Supports CAD model comparison for digital verification and inspection.
- Offers real-time data processing and reporting.
- Can perform Geometric Dimensional and Tolerancing analysis.
Rigid and Stable structure
- Manufactured with granite or steel bases for vibration resistance.
- Offers a stable platform for accurate measurements.
- Designed to reduce thermal expansion, ensuring consistent precision in fluctuating environmental conditions.
Advantages of CMM Machine (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
A Coordinate measuring machine or CMM machine is an essential instrument for ensuring accuracy in the production process. The reason behind this is its vast advantages in various industries, some of which are described below:
Increase efficiency and reduce costs
With its rapid and precise measurements, the CMM machine is essential in the production process. In the manufacturing industry, the manufacturing of critical tools is rapidly spreading. In this case, the CMM machine is a perfect instrument for measuring the dimensions. Lastly, they minimize production costs and time.
Ensured Quality Control
Other than measuring machine parts by using different conventional methods, coordinate measuring machines are highly reliable. It can provide different services by measuring and evaluating machine parts digitally. All these steps have been followed for better quality assurance.
Adaptable with various Probing systems and Methods
Coordinate measuring machines are highly adaptable with various types of tools and components. The detailed nature of the part has not been observed as the CMM machine will identify it.
Minimal Human Interaction
The coordinate measuring machine has no interaction with humans as it is a computer-controlled machine. It minimizes coordination with humans as it relies on the system. No involvement with humans can lead to the reduction of operational errors that may result in faults.
Disadvantages of Coordinate Measuring Machine
The Probe needs to contact the surface
When the probe is being used by the CMM machine, it consists of the same process. For the working of the probe, it must be attached properly to the surface of the part to be measured. For the robust parts, contact with the surface is not necessary. For parts that are soft and fragile, continuous probing can lead to material damage and fatigue.
Delicate Components Can Result in Faults
There are many soft materials, such as rubbers, and the parts that arise from such materials can result in material failure. This phase can lead to defects that are observed during digital analysis.
The Correct Probe Must Be Chosen
Coordinate measuring machines use different types of probes, but it is crucial to pick the right one. Choosing the correct probe based on the correct part’s dimension. What kind of design is needed, and what are the capabilities of the probe? These things must be remembered while selecting the correct probe.
Types of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)
Coordinate measuring machines are based on their features and structures, including the main type, the Bridge CMM, Gantry CMM, Cantilever CMM, Horizontal Arm CMM, and Optical CMM.
Bridge Coordinate Machines
The Bridge Coordinate Machines are the most common type. These are further classified into movable-table and movable-bridge designs. These machines are available in both fixed as well as portable configurations. Unlike laboratory-based models, shop-floor bridge coordinate measuring machines are hard to resist in industrial environments. However, they are particularly limited in measuring small to medium-sized components that can be placed on the table manually.
Gantry Coordinate Machines
These are designed for measuring large-scale components, such as automobiles and heavy machinery, where the floor itself serves as a datum. These machines remove the need to lift and position heavy parts on the table. Hence, they are ideal for large and bulky components. Their size and complexity make them more expensive than other machine types.
Cantilever Coordinate Machine
As they are supported at a single point, Cantilever machines are unique. These are less rigid compared to designs with two-point support. Due to this, they are generally limited to analyzing and evaluating small parts. However, their main advantage is unrestricted access from three sides, providing greater flexibility when inspecting parts compared to the other machine types.
Horizontal Arm CMM Machine
Horizontal Arm CMMs are designed for measuring large, lightweight, or sheet metal components. They feature a horizontally mounted probe, allowing easy access to tall or wide parts. Commonly used in automotive and aerospace industries, they offer flexibility and reach but are generally less rigid than bridge or gantry CMMs.
Optical Coordinate Measuring Machine
Optical Coordinate Measuring Machines (Optical CMMs) use vision systems, lasers, or white-light sensors to capture precise measurements without physical contact. Ideal for fragile or flexible components, they offer high-speed scanning and detailed surface analysis. Optical CMMs excel in non-destructive inspection, making them essential for the electronics, medical, and aerospace industries.
Applications of Coordinate Measuring Machines
A CMM machine or Coordinate Measuring Machine is used for dimensional inspection, reverse engineering, quality control, tool certification, and assembly verification. It is used across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial manufacturing industries. Here are its key applications:
Automotive Industry
CMM machines in the automotive industry ensure precise measurement of engine parts, chassis, and body panels, maintaining strict quality standards. They verify dimensional accuracy, alignment, and tolerances, reducing defects and improving safety. CMMs also support rapid prototyping, reverse engineering, and assembly validation, enhancing efficiency and reliability in vehicle production.
Aerospace Industry
CMM machines play a crucial role in the aerospace industry by ensuring precision and accuracy in manufacturing critical components like turbine blades, fuselage sections, and engine parts. They verify tight tolerances, conduct geometric inspections, and ensure compliance with aerospace standards, enhancing the safety, reliability, and performance of aircraft and spacecraft components.
Medical Industry
CMM machines play a crucial role in the medical industry by ensuring high-precision measurements for medical implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments. They verify dimensional accuracy, maintain strict quality standards, and support the non-destructive testing of delicate components, ensuring patient safety and compliance with medical regulatory requirements like FDA and ISO 13485.
Aircraft and Space Vehicles
CMM machines play a crucial role in the aircraft and space vehicle industry by ensuring precision, structural integrity, and quality control. They accurately measure aerospace components, fuselage sections, turbine blades, and critical engine parts, ensuring they meet strict tolerances. This enhances safety, performance, and reliability in aviation and space exploration applications.
FAQs
What are the features and uses of a Coordinate Measuring Machine?
Features of CMM Machine: High-precision measurement, multi-axis movement, contact/non-contact probes, automated inspection, and CAD integration.
Uses of CMM Machine: Ensures dimensional accuracy, quality control, reverse engineering, and geometric analysis in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
What are the 4 types of Coordinate Measuring Machines?
The four types of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) are Bridge, Gantry, Cantilever, and Portable CMMs. They vary in size, structure, and application, offering precision measurement for industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
What is the principle of CMM?
The principle of a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is based on 3D coordinate measurement using a probe system. It records the precise X, Y, and Z coordinates of an object’s surface to determine dimensional accuracy, ensuring compliance with design specifications. CMMs operate using contact or non-contact probing techniques for precise inspection.



